What are wetlands?
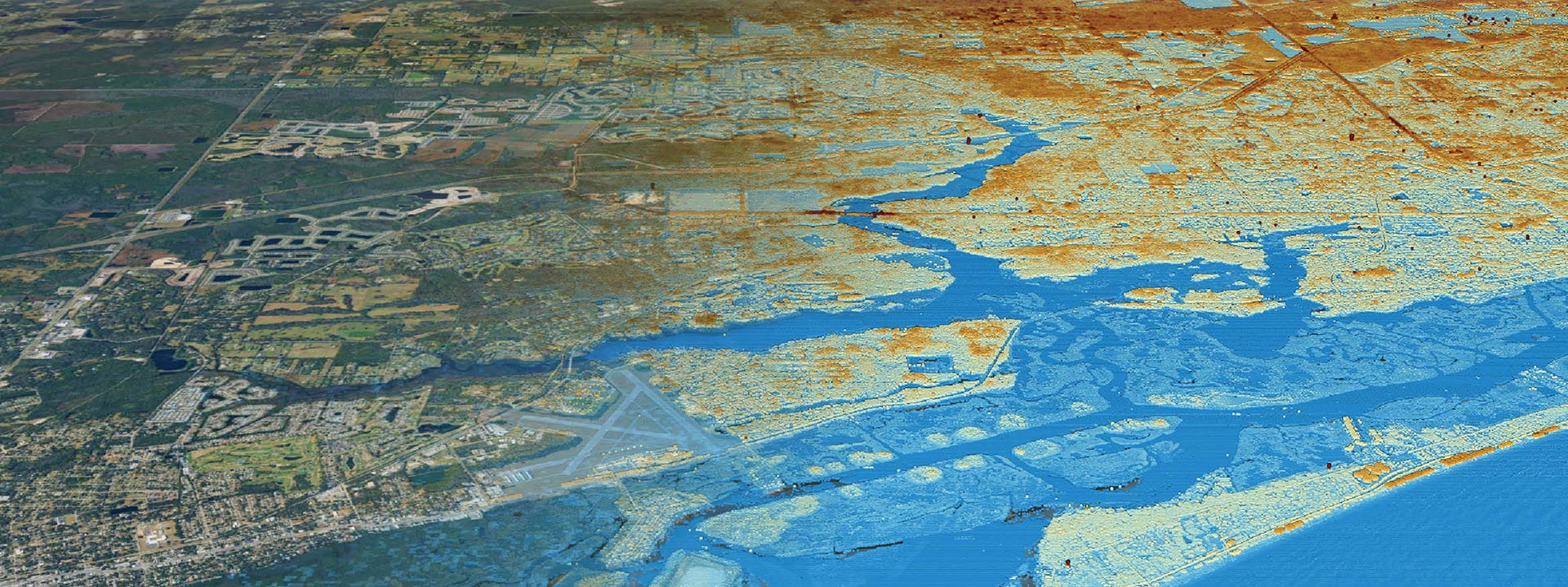
Wetlands are vital ecosystems that play a crucial role in maintaining a balanced and healthy environment. However, the term wetland can be vague and mean different things to different people, which is why it is important to have a technical definition to standardize the concept. In Florida, wetlands are defined as areas that are inundated or saturated by surface water or groundwater at a frequency and duration sufficient to support vegetation adapted for life in saturated soils. This vegetation typically includes hydrophytic macrophytes that are able to grow, reproduce or persist in aquatic environments or anaerobic soil conditions.
Florida wetlands encompass a variety of different types, including swamps, marshes, bogs, and mangrove swamps. They play a vital role in water filtration, flood control, and providing habitats for a diverse array of plant and animal species. It is important to protect and preserve wetlands, as they provide numerous benefits to both the environment and society.
The methodology for identifying and delineating wetlands is provided in Rule 62-340 F.A.C. This methodology is designed to further clarify and standardize the definition of wetlands, ensuring that they are properly identified and protected. Wetlands are a valuable resource, and it is important that we work together to preserve and protect them for future generations.