Business Case for Geospatial Technologies
As technology advances, businesses constantly seek new ways to streamline their operations and increase efficiency. One technology that has become increasingly popular in recent years is geographic information systems (GIS). GIS is a powerful tool that allows businesses to analyze and visualize data related to location, enabling them to make more informed decisions and gain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
For business owners who are unfamiliar with GIS, it may seem like a complicated and technical tool that only large corporations can afford to utilize. However, this is far from the truth. GIS can be a valuable asset for businesses of all sizes and industries, and it is becoming more accessible and user-friendly than ever before.
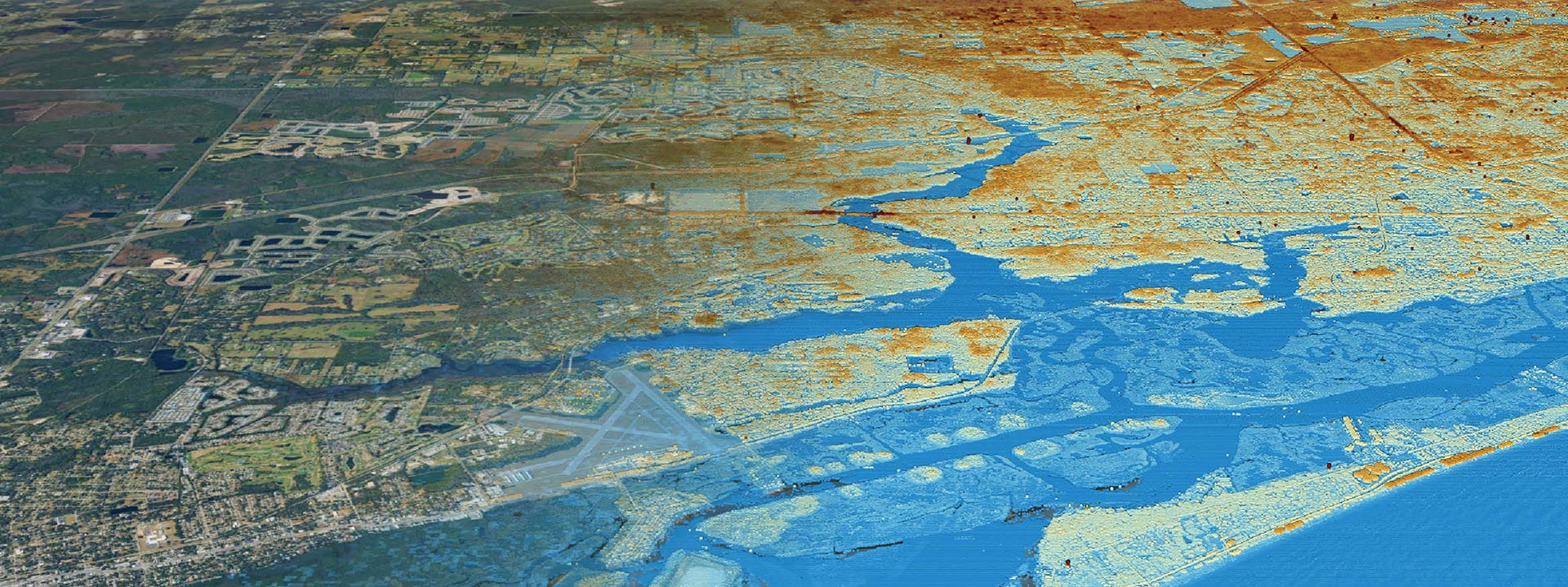
One of the main benefits of GIS is its ability to provide a spatial context to business data. This means that businesses can take data such as customer addresses, sales territories, and competitor locations and overlay it on a map to gain insights that would otherwise be difficult to see. For example, a retail business could use GIS to identify the most profitable locations for new stores based on factors such as demographics, traffic patterns, and competitor proximity.
GIS can also be used to improve operations and save businesses time and money. For example, a logistics company could use GIS to optimize delivery routes based on traffic patterns, road conditions, and delivery schedules, resulting in faster and more efficient deliveries. Similarly, construction companies can use GIS to monitor job sites, track equipment and inventory, and identify potential safety hazards.
Another advantage of GIS is its ability to facilitate collaboration and communication between different departments within a business. By visualizing data on a map, companies can more easily share information and insights between teams, leading to better decision-making and more efficient workflows.
In addition, GIS can be used to support marketing and advertising efforts. For example, a business could use GIS to target advertising to specific areas based on demographics, income levels, and other factors. This can lead to more effective advertising campaigns and higher returns on investment.
Overall, GIS is a powerful tool that can provide valuable insights and help businesses make more informed decisions. While the initial investment may seem daunting, the long-term benefits can far outweigh the costs. By utilizing GIS, businesses can gain a competitive edge and stay ahead in an ever-evolving marketplace. So, if you’re a business owner looking to improve operations, increase efficiency, and gain valuable insights, it’s time to explore what GIS can do for your organization.