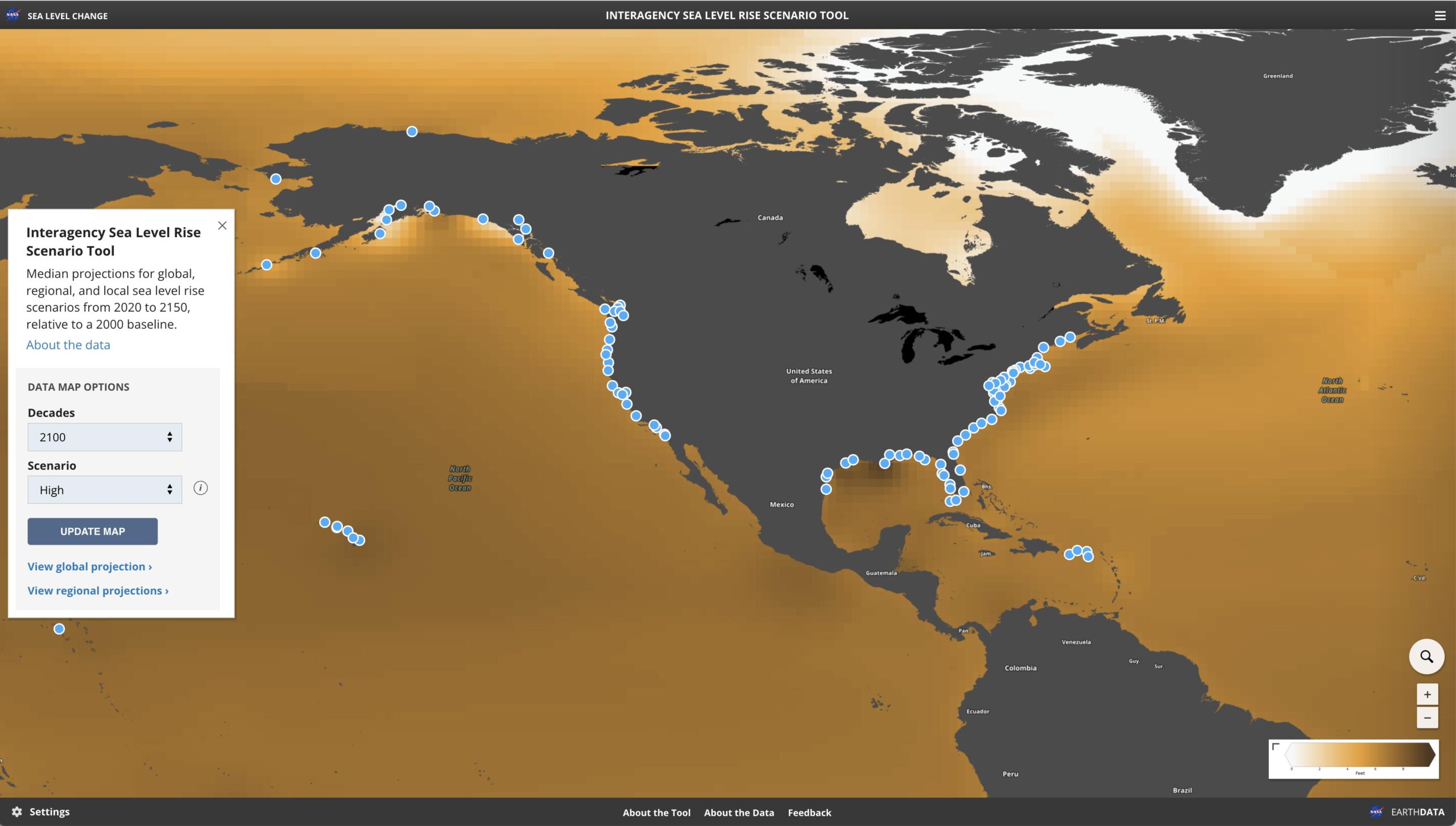
10 Uses of GIS and Geospatial Technology
GIS, or Geographic Information System, is a powerful tool that allows users to visualize, analyze, and interpret data in a geographic context. GIS has numerous applications in various fields and can be used for a variety of purposes. In this blog post, we will explore 10 different uses of GIS.
- Urban planning: GIS can be used to analyze and visualize data related to land use, transportation, and other factors to help plan and design sustainable cities.
- Natural resource management: GIS can be used to manage and analyze data related to forests, water resources, and other natural resources to make informed decisions about their management and conservation.
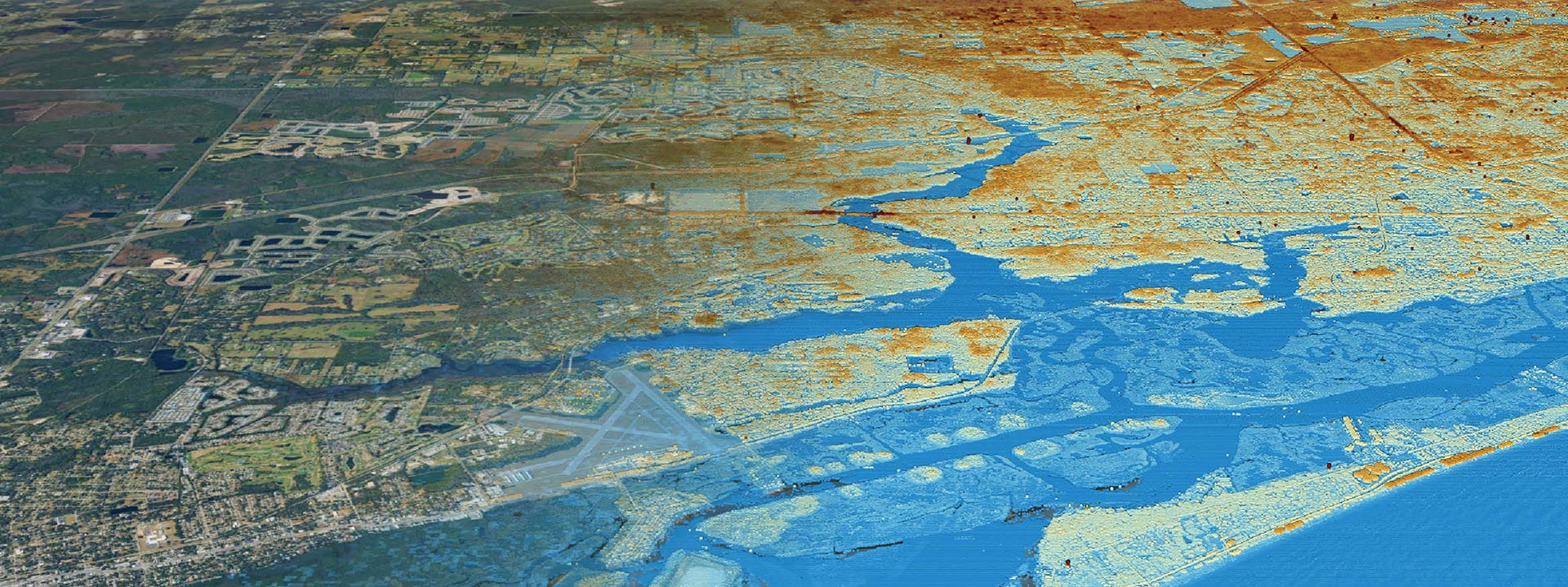
- Environmental monitoring: GIS can be used to monitor and analyze data related to air and water quality, climate change, and other environmental factors to understand their impact on the environment.
- Disaster response and management: GIS can be used to map and analyze data related to natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and wildfires to help emergency responders make informed decisions and allocate resources.
- Public health: GIS can be used to analyze data related to the spread of diseases, access to healthcare, and other factors to inform public health policies and interventions.
- Agriculture: GIS can be used to analyze and visualize data related to soil quality, weather patterns, and other factors to inform agricultural practices and improve crop yields.
- Business intelligence: GIS can be used to analyze data related to customer demographics, market trends, and other factors to inform business strategies and decision-making.
- Law enforcement: GIS can be used to map crime patterns, analyze data related to criminal activity, and help law enforcement agencies allocate resources and investigate crimes.
- Archaeology: GIS can be used to analyze and visualize data related to archaeological sites, helping archaeologists understand the spatial relationships between different artifacts and features.
- Education: GIS can be used in the classroom to teach geography, spatial analysis, and other subjects. Students can use GIS to analyze data, create maps, and visualize complex relationships.
In conclusion, GIS is a versatile tool that can be used in various fields and applications. From urban planning to education, GIS is already revolutionizing the way we analyze, interpret and interact with data. As technology advances, GIS will become even more prevalent in our daily lives, helping us make informed decisions and create a more sustainable future.